Risk management and capital allocation
The principles underlying SpareBank 1 SMN’s risk management are outlined in the Bank’s risk management policy. The Bank gives much emphasis to identifying, measuring, managing and following up central risks to ensure that the Group progresses in line with its adopted risk profile and strategies.
Risk management in the Group supports the Group’s strategic development and target attainment. Risk management will also ensure financial stability and prudent asset management. This will be achieved through:
- a strong organisation culture featuring a high level of risk-management awareness
- a sound understanding of the risks that drive earnings and risk costs, and thereby creating an improved basis for decision-making
- striving for an optimal use of capital within the adopted business strategy
- avoiding unexpected negative events which could be detrimental to the Group’s operations and reputation in the market.
The Group’s risk is quantified by calculating expected loss and the risk-adjusted capital (economic capital) needed to meet unexpected losses. Expected loss is the amount which statistically can be expected to be lost in a 12-month period. Risk-adjusted capital is the volume of capital the Group believes it needs to meet the actual risk incurred by the Group. The Board has decided that the risk-adjusted capital should cover 99.9 per cent of all possible unexpected losses.
Statistical methods are employed to compute expected loss and risk-adjusted capital. However, in some instances expert assessments are required. For risk types where no recognised methods of calculating capital needs are available, the Bank defines risk management limits to ensure that the likelihood of an event occurring is extremely low.
Return on risk-adjusted capital is a key strategic target of internal management at SpareBank 1 SMN. It entails allocating capital to business areas based on the estimated risk associated with the given business area, and continuously monitoring the return on capital. Calculation of risk-adjusted capital makes it possible to compare risk across risk groups and business areas. Risk is also gauged and monitored by measuring positions relative to quantitative risk limits and key portfolio risk limits.
The Group’s overall risk exposure and risk trend are monitored through periodic risk reports to the Administration and the Board of Directors. Overall risk monitoring and reporting are carried out by the Risk Management Division which is independent of the Group’s business areas.
Responsibility for risk management and control
Risk management and control are part of SpareBank 1 SMN’s corporate governance as described in the chapter on Corporate Governance. The Group’s control and management model aims for independence in risk reporting, with due emphasis given to responsibilities and roles in the day-to-day risk management. SpareBank 1 SMN has for several years devoted substantial resources to developing effective risk management processes in order to identify, measure and manage risk.
In the risk and capital management process, organisation culture is the foundation on which the other elements are built. SpareBank 1 SMN’s organisation culture comprises management philosophy, managerial style and the people making up the organisation with their individual qualities such as integrity, values, and ethical stance. A deficient organisation culture cannot be compensated for by imposing other management and control measures.
The Group emphasises a control and management structure that promotes targeted and independent management and control. The risk management process is three-tiered:
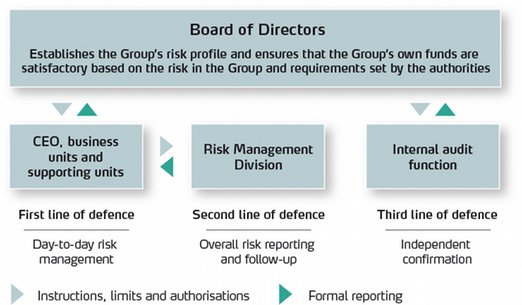
The Board of Directors of SpareBank 1 SMN is responsible for overseeing that the Group’s own funds are satisfactory based on the adopted risk profile and requirements set by the authorities.
The Group Board establishes the overarching objectives such as risk profile, return targets and the distribution of capital on the respective risk areas. The Board also establishes overall limits, authorisations and guidelines for risk management within the Group as well as all significant aspects of risk management models and decision-making processes.
The Group CEO is responsible for risk management hence monitoring risk exposure and the implementation of effective risk management systems in the Group. The Group CEO is also responsible for delegating authorisations and reporting to the Board.
The business areas are responsible for the day-to-day risk management within their respective areas, and they must at all times see to it that risk management and risk exposure comply with the limits and overarching management principles established by the Board or the Group CEO.
The Risk Management Department is organised independently of the business units and reports directly to the Group CEO. This department is responsible for the Group’s risk models and the further development of effective risk management systems. It is also responsible for independent risk assessments, risk reporting and for overall risk monitoring within the Group.
Credit Committees. The Group has one central-level Group Credit Committee and one Credit Committee for SMB customers.
The Credit Committees are responsible for delivering an independent recommendation to the authorisation holder concerned. The recommendation:
- assesses loan and credit applications according to the existing credit strategy, credit policy, lending regulations and credit processing routines
- gives particular emphasis to identifying risk related to the individual application and provides an independent credit risk assessment
- clarifies the consequences for the Group of the various risks involved
Special exposures. The Bank has a separate department for special exposures which takes over dealings with customers who are clearly unable, or highly likely to become unable, to service their debts unless action is taken beyond ordinary follow-up.
Credit Watch Committee. This committee’s main focus is on exposures at risk. The committee deals with exposures defined on a centralised watch list, mainly in excess of NOK 50m.
Validation Committee. This committee reviews, at minimum annually, the validation of the Bank’s IRB models. The committee also considers proposals for implementation of newly and further developed versions of the Bank’s IRB models. The committee submits recommendations to the Bank’s Board of Directors, which makes the final decision.
The Balance Sheet Committee is responsible for matters related to capital structure and liquidity risk, market risk, internal pricing of capital and compliance with limits established by the Board.
The Internal Audit is a tool for the Board of Directors and the Administration to oversee that the risk management process is targeted, effective and functions as intended. The Group’s internal audit is carried out by an external provider, thereby assuring the required independence, competence and capacity. The Internal Audit function reports to the Board of Directors.
The Internal Audit function’s reports and recommendations for improvements in Group risk management are continuously reviewed within the Group. The Internal Audit function reviews, regularly and at least annually, the IRB system, including the models underlying the calculation of risk parameters and application of and compliance with the Capital Requirements Regulations.
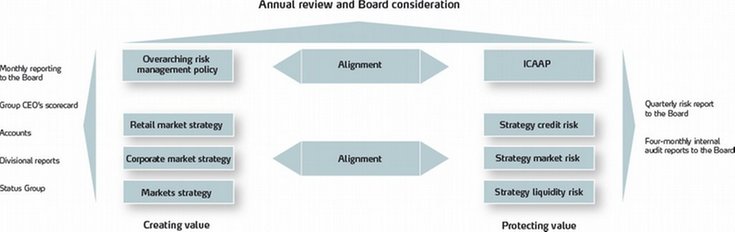
Capital management
SpareBank 1 SMN applies a focused capital management process designed to assure:
- effective capital procurement and capital application in relation to the Group’s strategic objectives and adopted business strategy
- satisfactory capital adequacy in relation to the chosen risk profile
- competitive returns
- competitive terms and good long-term access to capital market funding
- utilisation of growth potentials in the Group’s defined market area
- that no individual events can significantly impair the Group’s financial position.
A long-term objective of the adopted business strategy is to ensure that the risk-adjusted capital, to the extent it is possible, is allocated to those areas that yield the highest risk-adjusted return.
The capital management process has to:
- be risk-driven and include all significant types of risk within the Group
- be an integral part of the business strategy, management process and decision-making structure
- be forward-looking and include stress testing
- be based on recognised and appropriate risk measurement methods and procedures
- be regularly reviewed, at least annually, by the Board
Financial projections
Based on the strategic objectives and business plan, a four-year projection of financial developments is prepared. A projection is also made for a serious economic downturn scenario. The projections are designed to compute how financial developments in business activities and macroeconomy will impact on the Group’s financial development, including return on equity, the funding structure and capital adequacy.
Basel II and the IRB system
Finanstilsynet (the Norwegian Financial Supervisory Authority) has authorised SpareBank 1 SMN to use the IRB foundation approach for credit risk. The Bank applies accordingly its own classification models when computing regulatory capital requirements. The minimum capital requirement is 80 per cent of the requirement calculated under the old rules.
The IRB system includes models, processes, control mechanisms, IT systems and procedures and policies associated with classification and quantification of credit risk and with the extended management of credit risk. The IRB system and the models are validated quantitatively and qualitatively to ensure that the models have sufficient predictive ability and are aligned with adopted guidelines.
The Bank is authorised to use internal models in its risk management and capital calculations (IRB), and has applied to Finanstilsynet for permission to apply the advanced approach to its corporate loans. A response from Finanstilsynet is expected in mid-2014.
In 2013 SpareBank 1 SMN applied the standardised operational risk approach to quantify operational risk for the Parent Bank, and the standardised market risk approach to quantify market risk. SpareBank 1 SMN has established, as an integral part of its risk management policy, a capital allocation process (ICAAP) to ensure that the Bank at all times has adequate own funds in relation to its chosen risk profile. The process is also designed to ensure efficient acquisition and application of capital.
Credit risk
Credit risk is the risk of loss due to the inability or unwillingness of customers or counterparties to honour their commitments to the Group. The Bank’s organisation of and framework for management of credit risk is adapted to the Basel Committee’s Sound Practices for the Management of Credit Risk and to Finanstilsynet’s module for management and control of credit risk.
Credit risk arising from the Group’s lending activity is the largest area of risk facing the Group. The Group incurs exposure to credit risk through lending and leasing products to retail and corporate customers and through the operations of the Bank’s Markets and Finance Divisions.
Through its annual review of the Bank’s credit strategy, the Board of Directors concretises the Bank’s risk appetite by establishing objectives and limits for the Bank’s credit portfolio.
The Bank’s credit strategy and credit policy are derived from the Bank’s main strategy, and contain guidelines for the risk profile, including maximum expected loss (EL) for SMN Retail market and SMN Corporate market respectively, maximum portfolio default probability (PD) and maximum economic and regulatory capital (UL) allocated to the credit business. Concentration risk is managed by:
- limits on the size of loans and loss given default on individual exposures,
- limits on maximum exposure and application of economic capital within lines of business,
- limits on regulatory risk weighted assets (RWA) for Retail and Corporate markets and
- requirements regarding maximum exposure, credit quality and number of exposures above 10 per cent of own funds.
Compliance with credit strategy and limits set by the Board of Directors is monitored on a continual basis by the Risk Management and reported quarterly to the Board of Directors.
Credit risk is managed through:
a) Organisation of management and control of credit risk, established annually by the Board of Directors
The document establishes the overarching principles for lending. This includes the structuring of the Bank’s management documents, the organisation (distribution of responsibilities and roles) of the credit function and the overarching principles for lending.
b) The credit strategy, adopted annually by the Board of Directors
The credit strategy establishes priority areas, credit strategy limits and targets and how credit risk is to be priced at SpareBank 1 SMN
Credit risk management at SpareBank 1 SMN is based on the principles recommended by the Basel Committee’s paper entitled ‘Principles for the Management of Credit Risk’, capital adequacy rules (Basel II) and relevant statutes and regulations.
c) Guidelines for portfolio management
The guidelines describe the framework and guidelines that apply to the management of SpareBank 1 SMN’s credit portfolio. This applies to the distribution of responsibilities and roles in connection with the measurement and reporting of portfolio risk and profitability as well as measures suited to manage the portfolio within the framework defined in the credit strategy and credit policy.
The composition of the portfolio is managed through the establishment of principles and framework for the granting of new credits, or through changes in existing exposures.
d) Credit policy for the Retail and Corporate markets.
These documents describe how the Bank’s credit strategy is to be implemented through the establishment of detailed lending criteria for the Corporate and the Retail. The responsibility for developing and maintaining the credit policy rests with the Group CEO.
e) Lending regulations – exercise of lending authorisations
All authorisations within the Retail and Corporate markets are personal. In the Corporate market, credit committees have in addition been set up at local and central level to advise the decision maker in major credit cases. Granting of credit must be in line with the Bank’s credit strategy, credit policy, credit processing procedures and guidelines, and must be characterised by completeness, high quality and professionalism. This is documented in the Bank’s ordinary loan-officer system.
The Bank’s risk classification system is designed to enable the Bank’s loan portfolio to be managed in conformity with the Bank’s credit strategy and to secure the risk-adjusted return. The Board of Directors delegates overall lending authorisation to the Group CEO and the divisional directors. The Group CEO can further delegate authorisations to lower levels.
Lending authorisations are graded by size of commitment and risk profile.
f) Credit models
The Bank’s credit models are based on three central components: probability of default (PD), exposure at default (EAD) and loss given default (LGD).
Probability of default (PD)
The Bank’s credit models are based on statistical computations of probability of default. The calculations are based on scoring models that take into account financial position along with internal and external behavioural data. The models are based partly on point-in-time ratings and reflect the probability of default in the course of the next 12 months under the current economic conditions.
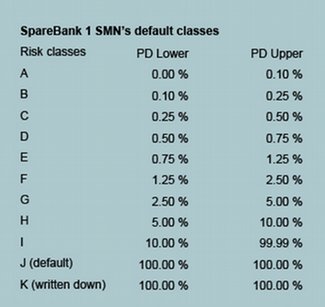
In order to group customers by probability of default, nine risk classes are employed (A-I). In addition the Bank has two risk classes (J and K) for customers whose loans are in default and/or written down. The following table shows the intervals employed for probability of default in each of the risk classes.
The figure below shows the volume distribution of exposures within the various risk classes.
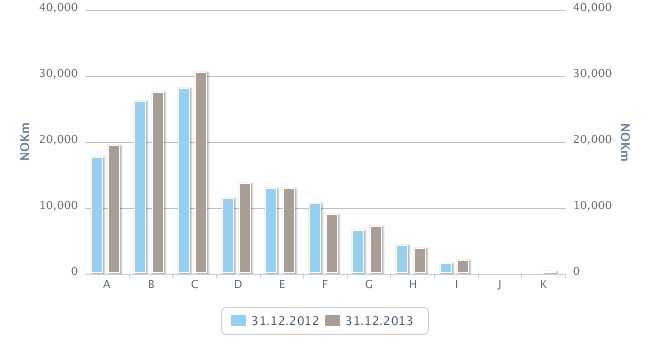
The Bank’s PD models for Retail and Corporate markets are validated on an ongoing basis and at minimum annually within three dimensions.
- Suitability. The models are evaluated in terms of their suitability for the Bank’s existing portfolio.
- Ranking ability. Through statistical methods (AUC) the models’ ability to distinguish between customers with differing risk levels is evaluated.
- Level. The models’ accuracy with regard to level is evaluated on an ongoing basis, at minimum annually. Where the estimated PD level deviates from the observed default rate (DR), the level will be adjusted. The evaluation takes into account the current economic situation and the model’s cyclical characteristics.
The results of the validation confirm that the model’s accuracy meets internal criteria and international recommendations.
Exposure at Default (EAD)
EAD is an estimate of the size of exposure in the event of any default at a specific date in the future. For drawing rights, a conversion factor (CF) is used to estimate how much of the present unutilised credit ceiling will be utilised at a future default date. For guarantees, CF is used to estimate what portion of issued guarantees will be brought to bear after default. CF is validated monthly for drawing rights within the Retail and Corporate markets. The Bank’s EAD model takes into account the differences between products and customer types.
Loss Given Default (LGD)
The Bank estimates the loss ratio for each loan based on the expected realisable value (RE value) of the underlying collateral, the recovery rate on unsecured debt as well as the direct costs of recovery. The LGD model and its components are validated at least annually against observed values from actual realisations.
In conformity with the Capital Requirements Regulations the estimates are downturn estimates. The values are determined based on defined models. Based on collateral cover (realisable value divided by EAD), the exposure is assigned to one of seven classes, the best of which has collateral cover above 120 per cent and the lowest has collateral cover below 20 per cent.
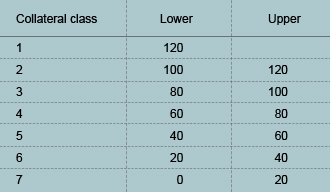
The three parameters above (PD, EAD and LGD) underlie the Group’s portfolio classification and statistical calculation of expected loss (EL) and necessary economic capital/risk-adjusted capital (UL).
The portfolio classification is designed to provide information on the level and development of overall credit risk in the total portfolio. Total exposures to customers and other counterparties are shown in notes to the accounts.
Counterparty risk
Counterparty risk in derivatives trading is managed through ISDA and CSA contracts set up with financial institutions that are the most used counterparties. The CSA contracts limit maximum exposure through market evaluation of the portfolio and margin calls when the change in portfolio value exceeds the maximum agreed limit or threshold amount. The Bank will continue to enter into CSA contracts to manage counterparty risk.
For customers, counterparty risk is hedged through use of cash depots or other collateral which must at all times exceed the market value of the customer’s portfolio. Special procedures have been established for calling for further collateral or to close positions if market values exceed 80 per cent of collateral values.
Market risk
Market risk is a generic term for the risk of loss and reduction of future incomes as a result of changes in observable rates or prices of financial instruments – in particular changes in share prices, bond rates, interest rates and exchange rates. Market risk also includes the risk of loss due to changes in the price of financial derivatives such as futures, options, and financial instruments based on items other than securities – for example commodities.
Market risk arises at SpareBank 1 SMN primarily as a results of the Bank’s investments in bonds, short-term money market papers and shares, and as a result of activities designed to underpin banking operations such as funding, fixed income and currency trading.
Market risk is managed through day-to-day monitoring of risk exposures against limits set by the Board of Directors and through ongoing analyses of outstanding positions. Risk Management reports monthly to the Board of Directors regarding compliance with the limits set by the Board. Detailed limits apply to investments in shares, bonds, positions in the fixed income and currency markets and limits to spread risk.
The Group defines limits on exposure to equity instruments using stress tests based on Finanstilsynet’s scenarios. The limits are reviewed at least once a year and are adopted yearly by the Bank’s Board of Directors.
The Bank uses Finanstilsynet’s models for market and credit risk to compute the Bank’s market risk. These models stress test the Bank’s market risk and are based on traditional risk measures with an addition for the risk factors risk diversification and market liquidity. Risk factors are reviewed annually.
Interest rate risk is the risk of loss due to changes in interest rates in financial markets. Interest rate risk arises mainly on fixed interest loans and funding in fixed interest securities. The risk on all interest rate positions expresses the change in value of interest rate instruments resulting from a rate change of 1 basis point. The Group utilises analyses showing the effect of this change for various maturity bands, with separate limits applying to interest rate exposure within each maturity band in addition to a separate limit for overall interest rate risk. Interest rate lock-ins on the Group’s instruments are essentially short, and the Group’s interest rate risk is low to moderate.
Spread risk is the risk of loss due to changes in the market value/realistic value of bonds. Bond risk is managed through an evaluation of the respective issuers. In addition the Bank has a separate limit for overall spread risk for all bonds. The Bank computes spread risk based on Finanstilsynet’s module for market and credit risk where overall loss potential is the sum of loss potentials for each individual credit risk exposure. The loss potential for the individual credit exposure is computed with a basis in rating and duration. Bond risk is considered to be moderate.
Exchange rate risk is the risk of loss due to changes in exchange rates. The Group measures exchange rate risk with a basis in net positions in the various currencies.
The limits on exchange rate risk are expressed as limits on the maximum aggregate currency position and on the maximum position in the individual currency. Exchange rate risk is considered to be low.
Equity risk is the risk of loss due to changes in share prices. This risk is linked to positions in equity instruments, including derivatives with equity instruments as the underlying. Equity risk is considered to be moderate.
Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Group will be unable to meet its obligations and/or finance increases in assets without extra costs in the form of falling prices of assets which must be realised or in the form of extra costly financing.
Management
The Bank’s finance function is responsible for the Group’s funding and liquidity management. Compliance with limits is monitored by the Risk Management Division which monthly reports to the Board of Directors. The Group manages its liquidity on an overall basis since the Finance Division is responsible for funding both the Bank and the subsidiaries.
Liquidity risk management is based in the Group’s overall liquidity strategy which reflects the Group’s moderate risk profile. As part of the strategy, a preparedness plan has been developed to handle the liquidity situation in periods of capital market turbulence with bank-specific and industry-related crisis outcomes separately and combined. Liquidity management includes stress tests which simulate the liquidity effect of various market events. The results of such testing are included in the preparedness plans developed for the Group’s and the alliance’s liquidity management regime.
Risk measurement
The Bank’s Board of Directors reviews the liquidity strategy annually and establishes a framework that promotes a long-term perspective and balance in liquidity procurement. This framework restricts the short-term maturity of the Bank’s liabilities within various time periods. Moreover, an aim of the Bank is to survive for 12 months with ordinary growth without fresh external funding.
The Bank’s most important source of finance is customer deposits. At end-2013 the Bank’s ratio of deposits to loans was 70 per cent. The Bank mitigates its liquidity risk by diversifying funding across a variety of markets, funding sources and instruments, and by using long-term funding. Too high concentration of maturities increases refinancing vulnerability. This risk is curbed through defined limits. The Bank is rated by Moody’s and Fitch to assure funding at acceptable prices in the money and capital markets.
SpareBank 1 SMN’s liquidity position is satisfactory. The Bank’s liquidity is measured regularly against the liquidity indicator for a reference portfolio defined by Finanstilsynet. The Bank’s liquidity strategy specifies a maximum deviation against this portfolio. The Bank stayed within this limit throughout 2013.
The figure below illustrates the funding portfolio’s maturity structure as from end-2013.
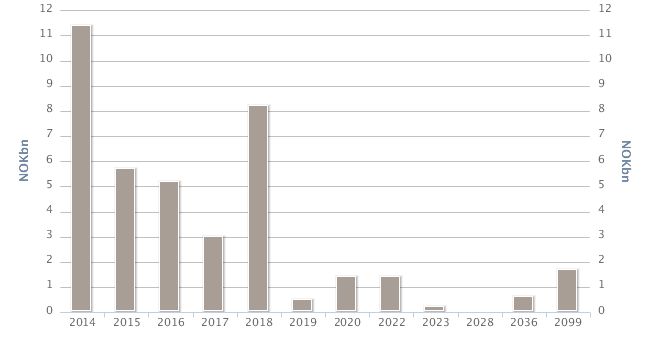
Development over the past year
The Bank was active in the funding market in 2013, and issued loans both domestically and abroad. The Group’s liquidity situation at end-2013 is satisfactory. The Group increased its liquid assets, in part through bonds deposited with Norges Bank in the course of the year. At year-end the Bank’s liquidity was satisfactory: NOK 5.3bn in cash and deposits with Norges Bank, NOK 1.8bn in loans and receivables from credit institutions and NOK 17bn in money market securities and bonds. The bulk of the securities portfolio can be used as collateral for loans from Norges Bank. Of the Group’s total funding volume at year-end, about NOK 11bn is to be refinanced in 2014. By end-2013 the Bank had moved NOK 31.7bn of its best-secured home mortgage loans to SpareBank 1 Boligkreditt. The Bank expects Boligkreditt to account for an important portion of the Bank’s financing in 2014.
In order to mitigate counterparty risk, the Bank has signed agreements concerning provision of collateral in connection with derivative trades (CSA contracts) with central counterparties. This will substantially reduce exposure to the Bank’s key counterparties since the Bank – or its counterparties – will be obliged to furnish collateral when the value of contracted business exceeds a pre-agreed threshold.
Operational risk
Operational risk is the risk of loss as a result of unsatisfactory or failing internal processes, systems, human errors or external events. Examples include errors on the part of employees, possible flaws in products, processes or systems, or the Bank may incur losses due to fraud, fire and natural damage.
Operational risk is a risk category that captures the bulk of costs associated with quality failings in the Bank’s ongoing business.
SpareBank 1 SMN wants to enhance its competence in operational risk management and closely cooperates with SpareBank 1 SR-Bank, SpareBank 1 Nord-Norge, Bank 1 Oslo Akershus, Sparebanken Hedmark and the University of Stavanger to further develop a framework for analysing operational risk and establish tools for improving quantification of operational risk exposures.
Identification, management and control of operational risk are integral aspects of executive responsibility at all levels in SpareBank 1 SMN. Executives’ most important aids in this respect are professional insight and managerial expertise along with action plans, control routines and good monitoring systems. A systematic focus on risk assessment also promotes knowledge and awareness of improvements needed in the particular unit. Any flaws found are reported to appropriate levels of the organisation along with recommended improvements.
SpareBank 1 SMN attaches importance to authorisation structures, good descriptions of procedures and clear definition of responsibilities in supply contracts between the respective divisions as elements of a framework for handling operational risk.
The Board of Directors is kept abreast of the operational risk position through quarterly risk reports and the yearly internal control report.
In addition the Board of Directors receives each year from the internal auditor an independent assessment of Group risk and whether the internal control system functions in an appropriate and satisfactory manner.
A system of registration and follow-up (Risk Information System) is used in the effort to ensure continuous improvement in all SpareBank 1 SMN’s business activities. This system promotes better structures and follow-up of risk, events and areas needing improvement. Together with the reporting carried out, this system constitutes an important experience base with respect to operational risk. All operational events which could potentially entail loss or where losses have arisen are recorded in the base. Improvement measures are considered and implemented where appropriate.
The Group has a broad-based insurance programme designed to capture significant portions of losses incurred as a result of major events and disasters. Various liability and crime insurances have established, along with property and contents insurances. These highly cost-effective policies are primarily intended to cover major loss events.
In 2013 the Parent Bank recorded operational loss events amounting to a total loss of about NOK 6m.
Owner risk
Owner risk is the risk that SpareBank 1 SMN will incur negative results on its holdings in strategically owned companies and/or must supply fresh equity to these companies. The companies concerned are defined in this context as companies in which SpareBank 1 SMN has a significant owner interest and influence.
SpareBank 1 Gruppen, BN Bank, SpareBank 1 Boligkreditt and SpareBank 1 Næringskreditt fall within this definition. While the risk posed by these companies is moderate, the Bank is indirectly exposed to increased market risk through its stake in SpareBank 1 Gruppen. SpareBank 1 Boligkreditt and SpareBank 1 Næringskreditt are primarily funding instruments for the core business operated by the owner banks. Their risk picture is relatively simple, and their appetite for market and liquidity risk is very low. Operational risk present in these companies is also low.
SpareBank 1 SMN exercises its control over the SpareBank 1 Gruppen and BN Bank effectively through the formal governing bodies that have been established.
Business risk
Business risk is the risk of unexpected income fluctuations arising from factors other than credit risk, market risk and operational risk. It can materialise in various business or product segments and can arise from business cycle fluctuations and changed customer behaviour.
Business risk is expresses through unexpected profit impairment. SpareBank 1 SMN constantly experiences changing framework conditions, both with regard to the competitive situation and the legislation affecting income models. The Bank’s response to all such changes is to adjust its business model to compensate for any lapse in income, either by identifying other income areas or adjusting costs to the new reality.
Sound strategic planning is the most important tool for mitigating business risk. Since business risk can arise from a variety of risk factors a broad set of tools (qualitative and quantitative) is employed to identify and report this type of risk.